28 Types of SNAKES That Live in Canada! (ID Guide)
There are A LOT of snakes in Canada!

And what’s interesting is that they are all incredibly unique and have adapted to fill many habitats and niches.
You’ll see that the snakes that live in Canada are very different from each other.
For example, some species are venomous, while others use constriction to immobilize their prey. Or the fact that certain snakes are rarely seen because they spend most of their time underground, but others are comfortable living EXTREMELY close to humans.
28 types of snakes in Canada!
#1. Timber Rattlesnake
- Crotalus horridus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults typically range from 75 to 150 centimeters in length.
- Coloration is variable and generally ranges from yellowish-brown to gray to almost black. Look for dark brown or black crossbands on their back.
- Heavy-bodied with characteristic rattle on the tail.
The Timber Rattlesnake, also known as the Canebrake Rattlesnake, is found in a few parts of Canada in Ontario. Look for these venomous snakes in lowland thickets, high areas around rivers and flood plains, agricultural areas, deciduous forests, and coniferous forests.
These snakes are ambush predators, waiting for unsuspecting prey to come within range of their strike. They feed primarily on small mammals but may also consume frogs, birds, and other smaller snakes. Timber Rattlesnakes strike their prey and release them, waiting until their venom has taken effect before eating them.
These venomous snakes are potentially the most dangerous species found in Canada due to their large size, long fangs, and high venom yield. Luckily, Timber Rattlesnakes have a mild disposition and don’t bite often. They typically give plenty of warning by rattling and posturing.

#2. Prairie Rattlesnake
- Crotalus viridis

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults typically range between 100 and 150 centimeters in length.
- Coloration is highly variable and can be greenish-gray, olive green, greenish-brown, light brown, or yellow. All variations have dark blotches on the body that turn into rings near the tail.
- Broad triangular head, elliptical pupils, heat-sensing pits between the eyes and nostrils, and a tail rattle.
These venomous snakes can be found in Canada in open prairies, grasslands, and forested environments.
Prairie Rattlesnake Range Map
The Prairie Rattlesnake hibernates during the winter, often in communal dens. These dens are typically rock crevices, caves, or old mammal burrows. Individual snakes return to the same den each winter and migrate up to seven miles to their hunting grounds in the spring.
When they feel threatened, these snakes freeze to use their camouflage to avoid detection. They may also quietly crawl away to cover. If approached, they may coil and rattle their tail as a warning before striking. Their potent venom has both hemotoxic and neurotoxic properties, and although rare, can be fatal to an adult human.

Prairie Rattlesnakes are listed on the ICUN Red List as a species of least concern. However, they are considered threatened and declining in parts of their range. In addition, they have faced pressure from habitat fragmentation and hunting.
#3. Eastern Massasauga
- Sistrurus catenatus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are typically around 60 centimeters in length.
- Coloration is gray or light brown with darker chocolate-brown blotches on the back and smaller ones on the sides, which feature light edges.
- Thick body, vertical pupils, heat-sensing pits between the eyes and nostrils, and heart-shaped head.
- Being rattlesnakes, look for the rattle at the end of their tail.
These small venomous snakes live primarily in wet habitats in Canada.
The name “Massasauga” actually comes from the Chippewa language and means “great river mouth” which describes their habitat. Look for them in floodplain forests, shrub swamps, low areas along rivers and lakes, wet prairies, moist grasslands, bogs, and marshes. During the summer, they often migrate to drier regions adjacent to these habitats.
Unlike other rattlesnakes, the Eastern Massasauga hibernates alone. They frequently hibernate in crayfish burrows but may also use small mammal burrows or spaces under rotting logs or tree roots. Dens must be below the frost line, or they risk freezing to death!
These snakes have cytotoxic venom (poisonous to cells), which destroys tissue, disrupts blood flow, and prevents clotting. But these snakes are secretive, shy, and avoid humans when possible. The only times they bite seem to be when handled or accidentally stepped on!

This venomous snake is listed as threatened, endangered, or a species of concern in all of its range. Historically, these snakes have faced pressure from hunting, and many states had bounties and roundups for them. Today they are still often killed out of fear AND face diminishing wetland habitats.
#4. Northern Watersnake
- Nerodia sipedon sipedon

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 60 to 140 centimeters in length.
- Coloration is pale grey to dark brown with reddish-brown to black bands.
- Large adults become darker with age and appear almost plain black or dark brown.
- Females tend to be larger than males, and coloration is most vivid in juvenile and wet individuals.
This species is the most common water snake in Canada!
Northern Watersnakes prefer slow-moving or standing water like ponds, lakes, vernal pools, marshes, and slow-moving rivers and streams. They’re most often seen basking on rocks or logs in or near the water.
These snakes primarily feed on fish and amphibians by hunting along the water’s edge and shallow water during the day. They grab their prey and quickly swallow while it’s still alive!
When disturbed, Northern Watersnakes flee into the water to escape. However, if grabbed or captured, they’re quick to defend themselves. They will release a foul-smelling musk from glands near the base of their tale, flatten their body, and strike the attacker.
While non-venomous, they can deliver a painful bite!

Their saliva contains a mild anticoagulant that can cause bites to bleed, making the injury appear worse. These important defense mechanisms help water snakes survive predators such as raccoons, snapping turtles, foxes, opossums, other snakes, and birds of prey.
#5. Queen Snake
-
Regina septemvittata

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are generally around 60 centimeters in length though individuals up to 90 centimeters have been reported.
- Coloration is drab brown or olive green with two lighter stripes down the sides.
- The underside is yellow or tan, with four dark stripes that run the length of their belly. No other similar species has this feature!
Queen Snakes prefer moving water and are generally found near streams and rivers with rocky bottoms. They have highly permeable skin, making them susceptible to evaporative water loss. As you can imagine, they are rarely spotted far from water.
Queen Snakes are considered less secretive than many other snakes in Canada.
They are primarily diurnal and can be spotted basking on rocks, overhanging branches, or vegetation near the water’s edge. They often take refuge under rocks along the edges of streams. If you’re lucky, you may see them swimming.
Queen Snakes are specialist predators that primarily feed on crayfish. They almost exclusively prey on newly molted crayfish, which have soft bodies and can’t use their pinchers yet. They hunt by probing under rocks and other submerged objects for crayfish.

#6. Eastern Garter Snake
- Thamnophis sirtalis sirtalis

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults typically range from 45 to 66 centimeters in length.
- Coloration varies and can be mixtures of green, brown, or black. Look for a distinct yellow or whitish stripe down the center of their back.
- Some individuals may exhibit a checkered body pattern.
- Subspecies of the Common Garter Snake.
Eastern Garter Snakes are common and easy to locate in Canada!
In fact, they are typically the snake species that people come across the most. They’re well-adapted to living around people and can often be found in city parks, farmland, cemeteries, and suburban lawns and gardens. Though not required, they prefer grassy environments near freshwater sources such as ponds, lakes, ditches, and streams.
Look for these snakes in Canada basking in the sun in grassy areas near cover.
Eastern Garter Snakes protect themselves when they are cornered or feel threatened. For example, if you capture or continually disturb one, it will defecate and release a foul-smelling musk from its glands. It’s also common for them to bite as a last resort!

The Eastern Garter Snake most commonly preys on toads, frogs, slugs, salamanders, fish, and worms. However, they are very opportunistic and will eat other insects and small animals they can overpower. They’re active during both the day and night, depending on the temperature.
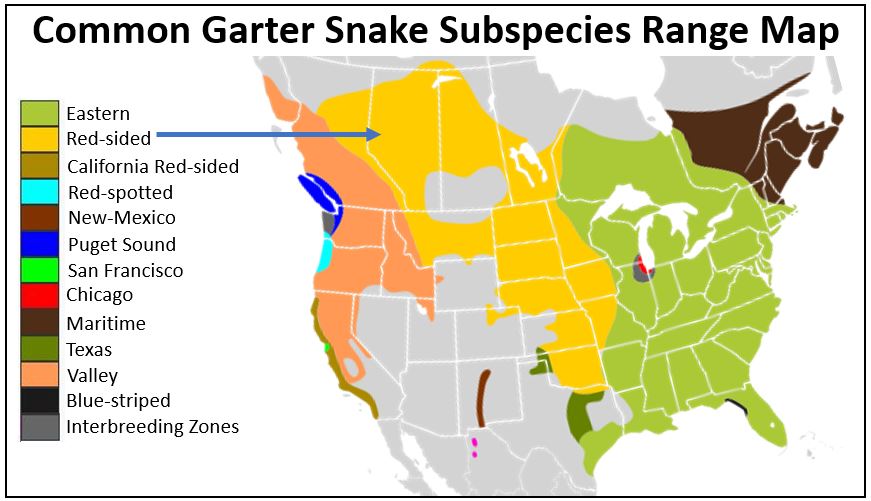
#7. Red-sided Garter Snake
- Thamnophis proximus parietalis

Identifying Characteristics:
- Normally dark green to black, but color varies.
- Three yellow stripes; one down the back and one down each side.
- As the name suggests, red or orange bars run along their sides between the yellow stripes.
- Subspecies of the Common Garter Snake.
Like other garter snakes, they are habitat generalists. Look for them in Canada everywhere, including forests, shrublands, wetlands, fields, and rocky areas. Their favorite foods include frogs, earthworms, and leeches! YUM! 🙂
In some areas, after emerging from hibernation, there are not enough females for all the males. In these cases, “mating frenzies” occur, and dozens and dozens of these snakes can be found together.
To survive colder months, Red-sided Garter Snakes have to hibernate BELOW the frost line. Depending on the area they are located in, it can be hard to find suitable locations. So the few adequate hibernation dens can shelter hundreds, even thousands, of snakes! To see an example, watch the video below:

#8. Eastern Ribbon Snake
- Thamnophis saurita

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults typically range from 45 to 66 centimeters in length. A slender snake with a long tail!
- Coloration is brown to nearly black with three bright yellow to cream stripes; one down the back and one down each side.
- Snout and entire head are brownish, lips and underneath head are white.
Did you see a slender snake in Canada with a long tail?
If so, it was probably an Eastern Ribbon Snake!
This species is semi-aquatic and RARELY found far from a source of water. Look for them in a wide variety of habitats, including marshes, grassy floodplains, streams, ditches with grass, wet areas in meadows, and woodlands adjacent to wetlands. Ribbon snakes are even found in suburban areas that match these conditions.
You might spot these snakes basking on branches of trees, bushes, or grasses overhanging the water. They typically hunt in the water and prey on amphibians, fish, and invertebrates.

When disturbed, these snakes quickly flee into grass or brushy areas. If caught, they are not aggressive and rarely bite. But you can expect them to defecate and spray musk onto your hands. In the wild, Eastern Ribbon Snakes rely on blending into their surroundings to escape predators.
#9. Terrestrial Garter Snake
- Thamnophis elegans

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 45 to 104 centimeters in length.
- Most adults have three yellow, light orange, or white stripes; one down their back and two down their sides.
- Coloration is widely variable. Individuals may be brownish or greenish. Some have red and black spots between the stripes, and occasionally all black individuals are found.
This snake can be difficult to identify in Canada!
Even trained herpetologists have issues! Its coloration varies widely, and there are believed to be 6 subspecies, although scientists still debate this.
Terrestrial Garter Snakes occupy various habitats, including both grasslands and forests. They can even be found in mountainous areas up to 3900 meters above sea level. As the name suggests, they’re primarily found on land. But interestingly, these garter snakes are great swimmers!

This species is the only garter snake in Canada with a tendency to constrict prey! Most garter snakes grab their prey quickly and just swallow, rubbing their prey against the ground if necessary.
Terrestrial Garter Snakes aren’t aggressive or dangerous, but they do possess mildly venomous saliva! It can cause a muscle infection or even kill some muscle tissue. Most bites on humans just cause pain and some swelling.
#10. Plains Garter Snake
- Thamnophis radix

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults average 90 centimeters in length.
- Coloration is gray-green with a distinctive orange stripe down the back and a greenish-yellow stripe down each side.
- Distinct light yellow spots on the very top of the head!
Plains Garter Snakes are almost always found in Canada in prairies and grasslands near freshwater sources. They have a fairly large population and adapt well to human-modified landscapes. You may spot them near abandoned buildings, trash heaps, or vacant lots.

This species is considered one of the most cold-tolerant of all snakes! In fact, they will even come out of hibernation on warmer winter days.

Plains Garter Snakes feed primarily on earthworms, slugs, and small amphibians. However, they have also been observed preying on small mammals and birds, including the Eastern Meadowlark and Bank Swallow.
#11. Valley Garter Snake
- Thamnophis sirtalis fitchi

Identifying Characteristics
- Adults range from 145 to 139 centimeters in length.
- Coloration is brown to black with three yellow stripes: one down the back and one down each side.
- Pronounced red bars between the yellow stripes. Yellowish chin, jaw, and belly, and a black head, which often has red sides.
- Subspecies of the Common Garter Snake.
Valley Garter Snakes are found in various habitats, including forests, wetlands, scrublands, fields, shorelines, and rocky areas. They’re also well adapted to humans and are often found in urban areas.
Look for these snakes in Canada under rocks, logs, and other objects, which they use for cover and thermoregulation. During the winter, they hibernate, often communally, below the frost line. They will use a variety of underground cavities, including mammal and crayfish burrows, rock crevices, ant mounds, and manmade spaces such as foundations and cisterns.
When disturbed, Valley Garter Snakes try to escape into the water and are excellent swimmers. If captured, be prepared for them to release musk and feces onto your hands! They may also strike, but only if they feel extremely threatened.
The Valley Garter Snake is considered a species of low risk. They are quite common and adapt well to human-modified habitats. However, they are frequently killed on roadways and are sometimes killed out of fear.
#12. Eastern Milksnake
- Lampropeltis triangulum triangulum

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults typically range from 60 to 90 centimeters in length.
- Coloration is tan or gray with 3 to 5 rows of reddish-brown, black-edged blotches.
- Look for a gray or tan Y- or V-shaped mark near the rear of the head.
Eastern Milksnakes get their unique name from an old myth that they milked cows since they’re commonly found in barns! Obviously, this isn’t true. Instead, their presence inside barns is likely due to the high number of mice, some of their favorite prey.
Eastern Milksnake Range Map
A member of the kingsnake family, Eastern Milksnakes occupy a wide variety of habitats in Canada, including fields, woodlands, agricultural areas, and rocky outcrops. These beautiful snakes are somewhat secretive and spend much of their time beneath the ground. You may be able to find one underneath rocks, logs, boards, and other debris.
The Eastern Milksnake prefers to feed on small mammals such as mice and shrews. However, they’ll also consume various types of prey, including birds and bird eggs, lizards, snakes, amphibians, fish, earthworms, slugs, insects, and carrion.

Like other individuals in the kingsnake family, they will prey on venomous pit vipers. So how do they combat the venom? Interestingly, their blood contains venom-neutralizing properties!
#13. Gray Ratsnake
- Pantherophis spiloides

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 106 to 182 centimeters in length though individuals up to 250 cm have been recorded.
- Coloration varies. Most Gray Ratsnakes are typically completely black.
- There may be red, white, or yellow flecking on the scales.
Look for Gray Ratsnakes in Canada in trees!
They are excellent climbers and often hunt and spend time in trees. Growing up, I used to see them all the time in a large walnut tree in our backyard! They occupy various habitats, including pinelands, stream banks, swamps, marshes, prairies, and agricultural areas.
They’re also spotted near barns and old buildings since these places provide them access to their favorite food, which is rodents. They are only found in Canada in parts of southern Ontario near Lake Erie and Lake Ontario.
Like other rat snakes, this species is an active hunter and a powerful constrictor. Adults typically feed on small mammals, birds, bird eggs, lizards, and frogs. They suffocate larger prey using their strong coils but often swallow smaller prey immediately.
#14. Smooth Greensnake
- Opheodrys vernalis
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are SLENDER and typically range from 35 to 50 centimeters in length.
- Coloration is uniformly light green with a yellow or white underside and a red tongue with a black tip.
- Juveniles may be olive-green, blue-gray, or even brown until they shed their skin for the first time.
Also called Grass Snakes, these bright green snakes can be found in marshes, meadows, pastures, savannas, open woods, and along stream and lake edges. They prefer moist areas near permanent water sources.
Smooth Greensnake Range Map

They prey almost exclusively on insects and spiders and don’t use constriction; instead quickly striking and swallowing their prey alive.
Smooth Greensnakes hibernate during the winter in Canada, seeking shelter in old mammal burrows and abandoned anthills. They often hibernate communally with other small snakes. They emerge in the spring, typically in April, and are active until October.

Smooth Greensnakes rely on their EXCELLENT camouflage to avoid predators. They’re also agile and can flee quickly if they must.
#15. Bullsnake
- Pituophis catenifer sayi

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are large and typically range from 120 to 180 centimeters long.
- Coloration is yellow, beige, or light brown with large brown, black, or reddish blotching on the back and three sets of small blotches on the sides.
- Blotches may appear like bands near the end of the tail, and the underside is yellowish with black spots.
These snakes are often seen in Canada in areas with high rodent populations.
You can find Bullsnakes in fields, grasslands, forest edges, savannas, and brushlands with sandy soils.

Bullsnakes are fast and can actively pursue prey in loose soil. They even use their prominent rostral (nose scale) to dig! Once they’ve captured their prey, they use their strong body to coil around and constrict their prey.
Despite being nonvenomous, these snakes act aggressively toward any threats. They often lift the front half of their body, hiss, and lunge at their attacker until they feel they can retreat.
Interestingly, their hissing can sound like a rattle! (see below!)

To accomplish this, the snake forces air through an extension of the windpipe, which has a piece of cartilage called an epiglottis that flaps back and forth, sounding very similar to a rattlesnake.
#16. Plains Hog-nosed Snake
- Heterodon nasicus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 38 to 99 centimeters in length.
- Coloration is varying shades of brown with darker brown blotches on the back, two alternating rows of smaller dark spots down the sides, and large longitudinal blotches on the sides of the neck.
- Enlarged rostral (nose) scale.
The Plains Hog-nosed Snake strongly prefers open sandy or gravelly habitats. They’re excellent burrowers and also use old animal burrows for hibernation and protection from hot temperatures. They are only found in small parts of southeast Alberta and southern Saskatchewan.
These snakes are best-known in mid-Canada for their displays when disturbed!
When initially confronted, Plains Hog-nosed Snakes typically remain motionless or hide their head under their coils. They may also try to bury themselves or escape into a burrow.
However, if they’re further disturbed, they’ll spread their jaws and neck like a cobra and puff up their bodies. They may also hiss loudly and deliver false strikes with a closed mouth.

If these intimidating displays fail, the Plains Hog-nosed Snake will then twist as though they’re in pain, roll over on their back and play dead. They’ll be limp, open mouthed, and will remain this way even if picked up. They may also bleed from the mouth and cloaca, expel musk and fecal matter, and regurgitate recently eaten food.
If I saw one of these snakes do this display, I’d definitely leave it alone! But, unfortunately, they’re sometimes killed by people who are frightened by their cobra-like posture.
#17. Eastern Hog-nosed Snake
- Heterodon platirhinos

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults typically range from 50 to 75 centimeters in length.
- Coloration can be yellow, gray, brown, black, olive, or orange, often with darker blotches or spots down its side and back, though solid gray and black individuals are fairly common.
- Thick-bodied, broad, triangle-shaped heads, and an upturned snout.
Eastern Hog-nosed Snakes prefer areas in Canada with sandy soil.
Here’s why:
Eastern Hog-nosed Snakes primarily prey on toads and use their upturned snout to dig for them in their burrows. They also have enlarged teeth at the rear of the upper jaw that they use to puncture and deflate toads that puff up when threatened. These snakes also have large adrenal glands, which secrete large amounts of hormones to counteract the toad’s potent skin poison!
When disturbed, Eastern Hog-nosed Snakes lift their head off the ground and flatten their neck like a cobra! They may also hiss and false strike with a closed mouth.
If this display fails to scare off a predator, then the snake will play dead. They’ll roll onto their back, let their tongue hang out, and emit musk from glands near the base of their tail. Interestingly, when the threat has left, the snake will right itself and continue as normal. 🙂
#18. Dekay’s Brownsnake
- Storeria dekayi

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults typically range from 15 to 33 centimeters in length.
- Coloration is light brown or gray to dark brown or black with two rows of dark spots down the back, which are sometimes linked.
- A dark streak down the head and may have a light stripe down the center of the back.
Dekay’s Brownsnakes occupy various terrestrial habitats as long as there’s plenty of cover available such as rocks, logs, boards, and all sorts of trash and organic debris. They’re often found in backyards and gardens under objects.
Dekay’s Brownsnake Range Map
These secretive, nocturnal snakes hunt during the evening and night, feeding primarily on slugs and earthworms. However, they’ve also been known to consume snails, insects, insect larvae, small tree frogs, tadpoles, frog eggs, spiders, and fish. Prey is typically grabbed and quickly swallowed alive.
These docile snakes usually don’t bite in defense. Instead, if captured, they often squirm vigorously or flatten their bodies and may release foul-smelling musk from glands near the base of their tail.
This species is considered common in most of its range and is not a major conservation concern. It adapts well to human development and has a reputation as a “city snake.” However, pesticide usage and clean-up of cover objects may reduce their populations in urban areas by reducing their habitat and food source.
#19. Western Rattlesnake
- Crotalus oreganus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adult size varies widely over their range, with the largest individuals being 180 centimeters in length.
- Coloration varies greatly and can be dark brown, yellowish, dark gray, or olive-brown.
- Triangular head, heat-sensing pits between the eyes and nostrils, dark stripe with white borders that runs from the eye towards the jaw.
Also known as the Northern Pacific Rattle Snake, this venomous species occupies a wide range of habitats in southwest Canada. They can be found in mountainous areas, woodlands, and grasslands. They also often occur in close proximity to humans.
Western Rattlesnake Range Map
Western Rattlesnakes have excellent camouflage and unique coloring, as these snakes show considerable variation. When they’re young, they have a distinct color pattern, but it fades over time as the snakes mature.
These snakes may be active during the day or night and are often curled, waiting to ambush a variety of prey. They’ll feed on small mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians. They may also eat bird eggs, and young snakes often feed on insects.

#20. Puget Sound Garter Snake
- Thamnophis sirtalis pickeringii

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 70 to 100 centimeters in length.
- Coloration is dark grey or black.
- Look for three yellow or bluish stripes; a narrow one down the back and one down each side.
This beautiful garter snake is a subspecies of the Common Garter Snake and can be found in southwest Canada. Look for them in forests, wetlands, shorelines, scrublands, fields, rocky areas, and urban areas. They’re typically spotted by rocks and logs, which they shelter under for thermoregulation.
As the name suggests, the Puget Sound Garter snake has a limited range. It is only found on Vancouver Island and the surrounding mainland coast in Canada and northwest Washington.

These garter snakes hibernate during the winter, often with other snakes of the same species. They’ll use a variety of underground cavities as long as they’re below the frost line. These include mammal and crayfish burrows, ant mounds, rock crevices, foundations, cisterns, and other human structures.
Luckily, this species adapts well to human activity, and they aren’t a high-risk species. Inside their small range, they are typically the most commonly seen snake. However, they are frequently hit on roads in urban areas, face habitat loss, and are sometimes killed out of fear.
#21. Maritime Garter Snake
- Thamnophis sirtalis pallidulus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults can reach 102 centimeters in length!
- Coloration varies but is typically dark green, brown, or black. The stripes that are common on other garter snake species are missing or poorly developed.
- Features a yellowish chin, upper jaw, and belly. Some individuals may display a checkered or speckled patterning on the back.
- Subspecies of the Common Garter Snake.
Maritime Garter Snakes adapt well to humans in eastern Canada!
They are habitat generalists and can be found almost everywhere! Look for them in forests, shrublands, fields, rocky areas, wetlands, shorelines, and urban and agricultural areas. They’re commonly spotted when moving rocks or logs, where they hide underneath for protection and thermoregulation.

To survive the harsh northern winters in Canada, these garter snakes hibernate below the frost line. They’ll utilize mammal and crayfish burrows, rock crevices, underground cavities, ant mounds, and manmade structures such as foundations. Interestingly, they often hibernate communally with other snakes!
This species isn’t considered threatened and can live to be TWENTY years old! They’re relatively common and can tolerate moderately disturbed human habitats well. However, populations near roads frequently have high road mortality rates.
#22. Northwestern Garter Snake
- Thamnophis ordinoides
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults average between 30 and 60 centimeters in length.
- COLORATION IS HIGHLY VARIABLE. Individuals can be blackish, olive, brownish, bluish, or gray, sometimes with a reddish tint.
- Typically has three stripes, one down the back and one down each side. The color of these stripes can be red, yellow, orange, tan, white, greenish, or blue; however, on certain snakes, the stripes may be dull, narrow, or absent!
The Northwestern Garter Snake prefers damp areas in southwestern Canada with lots of vegetation and open sunny areas. They may be spotted near houses and are often found when moving boards, logs, or other objects that they use for cover.
This species is predominantly terrestrial. However, these garter snakes can swim, and some local individuals have been observed hunting in the water! They feed mainly on slugs and earthworms, but they also prey on snails, small amphibians, and possibly fish.
The Northwestern Garter Snake will typically flee into dense vegetation if disturbed. One study found that individuals with stripes usually move away quickly because their stripes make it difficult for predators to determine their speed. But plain or spotted individuals frequently freeze while fleeing because their excellent camouflage helps them blend in while they’re motionless.
#23. Butler’s Garter Snake
- Thamnophis butleri

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are slender and range from 38 to 51 centimeters in length.
- Coloration ranges from olive-brown to black with three yellow to orange stripes, one down the back and one down each side.
- Two rows of dark spots may be visible between the back and side stripes, and the head is usually small.
This species looks almost identical to Eastern Garter Snakes in Canada.
So how do you tell the difference?
What’s unique to Butler’s Garter Snakes is the placement of their side stripes! Technically speaking, they are centered on the third scale row up from the large, elongated scales on the underside of the body. The side stripes also overlap the adjacent second and fourth scale rows.
But unless you’re a herpetologist or want to inspect a snake closely, this probably means nothing to you. For the rest of us, their head is typically a bit small compared to other garter snakes. In addition, when they are threatened, instead of fleeing, they tend to thrash around in place.
This species is considered endangered in parts of its range. Industrial development of agricultural land has caused significant habitat loss and degradation in their range. If you want to find one, look in moist grassy habitats, typically under cover objects like rocks, logs, boards, and other debris.
#24. Eastern Foxsnake
- Pantherophis vulpinus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 90 to 180 centimeters in length.
- Coloration is light golden brown, yellow, or bronze with dark brown or reddish-brown blotches down the back and alternating spots down the side.
- Look for a short, flattened snout.
Eastern Foxsnakes are most often found in parts of Canada in grasslands, prairies, and farming areas. They much prefer wet areas as opposed to dry and are typically spotted on the ground. But don’t be surprised if you see one of these snakes in a tree, as they are strong, agile climbers.
These snakes are typically diurnal, but they may hunt at night during extremely hot weather. They often hide under rocks, logs, or in burrows to regulate their temperature. During the winter, they hibernate below the frost line in underground burrows.
Foxsnake Range Map

Eastern and Western Foxsnakes are closely related and look the same. In the past, they were even considered the same species before eventually being split apart. The best way to determine the correct species is by location, as they are divided by the Mississippi River.
If disturbed, Eastern Foxsnakes coil and vibrate their tail, producing a rattlesnake-like sound in dry leaves. If grabbed, they will often release a foul-smelling musk which is thought to smell like a Red Fox, giving them their name.

#25. Red-bellied Snake
- Storeria occipitomaculata

Identifying Characteristics:
- A small woodland species that grows between 10 to 25 cm (4-10 in) long.
- Colors vary from orange, gray, black, and brown.
- Their bright red or orange belly stands out from other species.
This species is probably the “cutest” snake in Canada!
Red-bellied Snakes are small, docile, and have a bright red belly, which makes them VERY easy to identify.
Look for them under logs and leaf litter. They are also commonly found burrowed inside abandoned ant mounds. They are typically diurnal but can be hard to find due to their secretive nature.
Red-belled Snake Range Map
The colors represent the different subspecies of Storeria occipitomaculata.
Red-bellied Snakes have a unique behavior called “lip-curling,” where they curl their lips upward and flick their tongue when eating or feeling threatened. This behavior helps them catch their prey and also scares off potential predators.
Unfortunately, people often kill this species out of fear. This is incredibly sad because these snakes are harmless and valuable to the ecosystem. In addition to this senseless slaughter, many are killed while crossing roads.
#26. North American Racer
- Coluber constrictor

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults typically range from 50 to 152 cm (20 to 60 in) in total length
- The patterns and texture of their skin vary widely among subspecies. However, most are solid-colored and have a lighter-colored underbelly.
True to their name, North American Racers are one of the FASTEST snakes in Canada!
When they get moving, they can speed away at up to 3.5 miles per hour (5.6 kph). These active snakes are curious and have excellent vision. In fact, they are known to raise their heads above the height of the grass to view their surroundings.
Despite their scientific name (constrictor), North American Racers do not squeeze their prey to death. Instead, they subdue their victim by holding it down with their body. Smaller prey is simply swallowed alive.
North American Racer Range Map
These nonvenomous snakes fight back incredibly hard if they feel threatened or become trapped. You can expect them to bite, thrash, defecate, and release a foul-smelling musk, especially if you try holding one. In addition, racers will try to impersonate rattlesnakes by shaking their tails in dry leaves.
North American Racers are still abundant in many places. But they face threats as they are losing habitat to urbanization and development. Unfortunately, many people also kill them out of fear, even though they are completely harmless, especially if you leave them alone.
#27. Ring-necked Snake
- Diadophis punctatus

Identifying Characteristics:
- These snakes are usually solid olive, brown, bluish-gray, or smoky colored. Look for a distinctive yellow or red neckband.
- The snake’s head color is usually slightly darker than the rest of the body, tending towards black rather than gray or olive.
- Adults are usually between 25-38 cm (10-15 in) long.
It can be hard to find these snakes in Canada!
That’s because Ring-necked Snakes are VERY secretive and spend most of their time hiding in areas with lots of cover. In addition, they are nocturnal and rarely seen during the day.
Ring-necked Snake Range Map
The colors represent the different subspecies of Diadophis punctatus.
If you come across one, you may see its unique defense posture. Red-bellied Snakes will curl their tails and expose their bright red-orange bellies when they feel threatened in hopes of scaring you away.
Ring-necked Snakes mostly eat small salamanders, earthworms, and slugs. Not much is known about their population status because they are so hard to find!
#28. Northern Rubber Boa
- Charina bottae
Also known as the Coastal Rubber Boa.

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are between 38-84 cm (1.25 to 2.76 ft.) long.
- They have smooth and shiny scales, and their skin is typically tan to dark brown with a lighter belly.
- One of the most noticeable features of rubber boas is their short and blunt tails, which are often confused for their heads.
As the name suggests, rubber boas get their name from their loose, wrinkled skin that looks and feels like rubber.
Northern Rubber Boas can thrive in diverse habitats in Canada, ranging from grasslands, meadows, and chaparrals to deciduous and coniferous forests and high alpine environments. One place you WON’T find this snake is in hot and dry areas, as they cannot tolerate higher temperatures.
The best place to find one is typically under shelter, such as rocks, logs, leaf litter, and burrows.
Northern Rubber Boas are often used to assist individuals in overcoming their fear of snakes. These gentle snakes never attempt to strike or bite humans under any circumstances. However, on rare occasions, they might emit a strong musk from their vent if they sense danger.
Do you need additional help identifying snakes in Canada?
Try this field guide!
Which of these SNAKES have you seen before in Canada?
Leave a comment below!
Also, if you enjoy this article, make sure to check out these other Canada guides!