24 Types of MAMMALS Found in Florida! (2025)
Do you want to learn about the mammals that live in Florida?

Luckily, you’ve come to the right place!
I have compiled a list of the most common and interesting mammals in Florida, with photos, facts, and RANGE MAPS. As you will see, there are lots of species, each with different and interesting habits and traits.
23 types of MAMMALS found in Florida!
#1. American Black Bear
- Ursus americanus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 5 to 6 feet tall and weigh 200 to 600 pounds.
- Coloration ranges from mostly black on the east coast to brown, cinnamon, or blonde in the west, and blue-gray or even creamy white in some populations.
- They have a flat back, small head, rounded ears, and non-retractable claws.
American Black Bears occupy various habitats in Florida but generally prefer inaccessible terrain.
Black bears are sometimes considered a nuisance because they sometimes damage cornfields, honeybee hives, and berry farms. In addition, they’re easily attracted to garbage, bird feeders, and coolers. Make sure to NEVER feed them, as this can make the bear not afraid of humans, which is dangerous for both people AND the bear.
Generally, Black Bears are timid around people. Unlike grizzly bears, females with cubs rarely attack people, often just sending their cubs up a tree so that they can retreat safely.
Black Bears are naturally active in the evening and early morning but sometimes alter their activity patterns for food availability. Bears may become active during the day when garbage and other human food sources are available. Black Bears in campgrounds often develop nocturnal activity patterns.
Despite the common belief, Black Bears in Florida don’t truly hibernate.
Instead, they enter a state of shallow torpor. In this state, their body temperature decreases, their metabolism slows, and they don’t need to wake to eat, drink, urinate, or defecate. Consequently, Black Bears must put on a heavy layer of fat in the fall to survive through winter and spring.
#2. White-Tailed Deer
- Odocoileus virginianus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 63 to 87 inches long and stand between 31 and 39 inches tall at the shoulder.
- Their coloring is tan or brown during the summer and grayish in winter, with white on the throat, chest, and underside of the tail.
- The males have antlers which they shed in the winter.
The White-tailed Deer is the most numerous large mammal in Florida!
White-tailed deer have an extensive range in North America and are able to thrive in various habitats, including coniferous, mixed, and deciduous forests, sawgrass and hammock swamps, cactus and thorn brush deserts, brushy areas, and farmlands. You’re most likely to see White-tailed Deer around dawn and dusk when they forage.
They are also completely comfortable in suburban environments, and it’s common for them to live in small wooded parks near housing developments. The herd in my neighborhood is particularly fond of our bird feeders. They stop by for a snack almost every evening!
There aren’t many things cuter than a baby deer! The fawns are born with white spots and are able to walk almost right away. The does may leave the fawns to forage for hours at a time. While their mother is away, the fawns lay flat on the ground with their necks outstretched and are well camouflaged. The female deer always come back to the baby, so make sure not to disturb the fawn if you find one!
#3. Wild Boar
- Sus scrofa

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 5 to 8 feet in length and weigh between 145 and 600 pounds.
- Their thick, coarse hair ranges in color from black to reddish-brown.
- They have large heads and necks and relatively short legs. Males have long bristly hairs down the middle of their back and large canines that protrude from the mouths of adult males.
Wild Boars occupy various habitats but prefer areas with water sources and some dense vegetation for shelter. They generally don’t thrive in habitats with extreme heat or cold.
Wild Boars are omnivores and what they eat varies with season and location. They consume large amounts of plant matter, including fruits, nuts, roots, herbaceous plants, and crops. They’re also known to eat bird eggs, carrion, small rodents, insects, and worms. Their voracious appetite can be very detrimental to an ecosystem, causing a loss of plant diversity and extensive soil erosion.
Wild Boars are invasive mammals in Florida, as they were introduced from overseas. Their population has exploded in the last 50-100 years, leading wildlife departments to put population control programs in place.
#4. Bobcat
- Lynx rufus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults weigh 15 to 35 pounds, stand 18 to 24 inches tall, and measure 28 to 47 inches in length.
- Their coloring is buff to brown, sometimes with a reddish tint, and black and brown spots and stripes.
- They have facial ruffs, ear tufts, white spots, and short, bobbed tails.
Bobcats are solitary, elusive, and shy mammals that are rarely seen in Florida.
These cats are highly adaptable and found in various habitats. They may be seen in residential areas. However, they generally avoid extensively cleared agricultural lands.
As carnivores, Bobcats are highly skilled hunters. They can climb, run up to 30 miles per hour, and leap high enough to grab low-flying birds. They patiently stalk their prey until they are close enough to pounce.
The largest threat to Bobcat populations is habitat fragmentation due to their large home ranges and elusive nature. However, rodenticides can also cause issues in populations when they feed on contaminated prey.
#5. Cougar
- Puma concolor

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults stand 24 to 35 inches tall at the shoulder and weigh between 64 and 220 pounds.
- Coloration ranges from reddish-brown to tawny or gray, with a black tip on their tail.
- They have round heads, pointed ears, and powerful forequarters.
Their large hind legs and massive paws help give Cougars incredible athletic ability. They can jump 15 feet high and 40 feet in distance and sprint at 50 miles per hour. Yet, despite their impressive speed, they generally wait and ambush prey.
Except for females raising young, adult Cougars generally only kill one large animal every couple weeks. Then, they drag the kill to a preferred area and cover it with brush, returning to feed off it over a few days.
While cougars don’t have predators besides humans, they may get into territory conflicts with other large predators. Cougars dominate one-on-one confrontations with wolves but are weaker when confronting packs. Generally, brown and black bears can drive off cougars with little effort.
Cougars have the most amount of names of any mammal found in Florida.
While Cougar seems to be the most common, these large cats are also known as catamount, mountain lion, puma, ghost cat, and panther.
#6. Red Fox
- Vulpes vulpes

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 18 to 35 inches in length and weigh 7 to 31 pounds.
- Their coloring ranges from pale orange or red to deep reddish-brown on their upper parts with white on their underside.
- They have black feet, a fluffy white-tipped tail, and large, pointy, black-tipped ears.
Red Foxes are arguably the most beautiful mammal in Florida!
These canines are often thought of as cunning and smart, with good reason! They’re excellent hunters and foragers. They also cache food and are adept at relocating it. Although they prefer rabbits, fish, and berries, they won’t hesitate to eat anything readily available.
This species has a distinctive way of hunting mice and other small rodents. Once the prey has been detected, they stand motionless, waiting and listening. Then they leap high into the air and bring their forelegs straight down, pinning the rodent.
Once baby foxes, known as kits, reach adulthood, their biggest threat is humans, who hunt and trap them for fur or kill them to protect livestock, such as chickens. Red Foxes can live 10 to 12 years in captivity but average only about three years in the wild.
#7. Gray Fox
- Urocyon cinereoargenteus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 31.5 to 44.3 inches long and stand 12 to 16 inches tall.
- Their fur is peppery gray on top and reddish brown everywhere else.
- They have a pointed muzzle and ears, long hooked claws, and a bushy tail with a black stripe on top.
Gray Foxes live in deciduous forests in Florida with a mix of brushy and woodland areas. They occasionally visit agricultural lands, but not as frequently as Red Foxes. Gray Foxes also prefer habitats with access to water, so you’re more likely to see them near rivers or lakes.
You’ll have a tough time finding this species, since they are primarily nocturnal and incredibly skittish of people. During the winter breeding season from December through March, they socialize with their mates but spend little time with other foxes.
Females give birth to litters of one to seven pups in the den, and the fathers provide most of their food after they are weaned. Males teach their pups hunting skills by practicing pouncing and stalking, and they begin to hunt at around four months of age.
#8. Coyote
- Canis latrans

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range in length from 3 to 4.5 feet and weigh between 15 and 44 pounds.
- Their coloring is grayish to yellow-brown on top with white underparts.
- They have a bushy tail, large, triangular ears, narrow muzzle, black nose, and yellow eyes.
Coyotes have a large range in North America and are found in various habitats, from the tropics to the tundra. Coyotes expanded their range after the near extermination of wolves and cougars by European settlers.
As with habitat, coyotes are highly versatile in their food selection. Despite being primarily carnivorous, they consume various plants, including berries, grass, and food crops. They will eat almost anything, and this extensive menu allows them to thrive in nearly every environment in Florida!
Even if you haven’t seen one, you’ve probably heard a Coyote before! They’re extremely vocal and communicate through howls, yips, whines, and barks. These vocalizations are used to warn pack mates of danger, greet each other, and play.
Sadly, Coyotes are commonly hunted and trapped for fur and sport.
#9. Eastern Cottontail
- Sylvilagus floridanus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are about 16.5 inches long and weigh up to 3 pounds.
- Their coloring is reddish-brown on the upper body with white on the underparts and tail.
- They have distinctive, large eyes and a round, fluffy tail.
These small mammals are vulnerable to many predators in Florida, so they require a habitat with good cover. Areas with a mix of grasses, dense shrub thickets, blackberry bushes, and brush piles are ideal. Well-drained fields with dense grass cover are often used for nesting.
One of their favorite places to nest is suburban yards! So, if you notice Eastern Cottontails hanging around your property, be careful when you mow your lawn. Although rabbit nests are usually slightly below ground level, lawn equipment is still dangerous for baby rabbits and mothers.
Eastern Cottontails consume a wide range of plant materials. They can be a nuisance for gardeners by eating garden plants and flowers. However, in winter, they eat woody materials from birch, oak, dogwood, sumac, and maple trees.
If threatened, Eastern Cottontails either freeze or flush. When they flush, they will run to cover in a zig-zag pattern reaching speeds up to 18 miles per hour. If grabbed, they may give a loud distress cry to startle a predator into releasing them.
#10. Striped Skunk
- Mephitis mephitis

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 18 to 32 inches long.
- Their coloring is black with two thick white stripes running down the back and tail and a thin white stripe from snout to forehead.
- They have a bushy black tail, small triangular heads, short ears, and black eyes.
Striped Skunks have perhaps the worst reputation of any mammal in Florida.
They’re best known for their unusual defense system. When threatened, a Striped Skunk will first stomp its feet or handstand as a warning. If these aren’t heeded, the skunk bends its hindquarters to face the animal and releases its defensive smelly spray. The unpleasant, oily liquid can reach up to 20 feet and may cause nausea, intense pain, and temporary blindness.
Despite their foul odor, Striped Skunks provide benefits to humans in the form of pest control. In the summer, they’re largely insectivorous and feed heavily on grasshoppers, crickets, beetles, and bees. The best thing to do if you see a skunk is to give it space. They usually move on quickly when they notice humans!
Striped Skunks have stable and abundant populations. However, some local populations have been affected by rabies outbreaks. In addition, Striped Skunks face threats from severe weather, chemical exposure, and vehicle collisions.
These small mammals are typically very common in suburban areas but are rarely seen because they are nocturnal. As seen below, they often visit bird feeders to eat leftover seeds on the ground!

#11. Eastern Spotted Skunk
- Spilogale putorius

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are 14 to 24 inches long.
- They have long, soft, glossy, black fur with white spots and stripes on the ears and back.
- They have a small head, short legs, and a prominent, black, long-haired tail.
Eastern Spotted Skunks are found in various open habitats, including mature forests that provide adequate cover. They may also occupy agricultural areas and use buildings, corn cribs, rock piles, haystacks, and other debris for cover and den sites.
Although their preferred food during summer is insects, Eastern Spotted Skunks are omnivores. During the fall and winter, they feed on equal amounts of plant and animal matter. They consume bees and wasps, larvae, and honey. They will also eat other insects, eggs, and small animals.
When threatened, Eastern Spotted Skunks will often assume a defensive posture in which they do a handstand on their front legs with their tail straight up and back legs spread apart in the air. They can balance and move forward in this stance while aiming specialized glands at the predator. If this display doesn’t work, then they spray a smelly deterrent.
The population of these small mammals is believed to have declined by more than 90% in Florida since the 1940s. As a result, they are listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List of Endangered Species. Contributing factors include unregulated over-hunting and trapping, habitat loss and fragmentation, widespread pesticide use, increased pressure from predators, and disease.
#12. Raccoon
- Procyon lotor

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are about 3 feet long and weigh between 15 and 40 pounds, though some males grow to over 60 pounds.
- Their fur is grayish-brown with 4 to 6 black rings on the tail and a black “mask” marking around the eyes.
- They have bushy tails and paws with five long, finger-like toes.
These mammals are one of the most common in Florida!
Due to their ability to adapt to humans, Raccoons have an extensive range and are found in forests, wetlands, suburbs, parks, and cities. They generally avoid large open areas and thrive in areas with water sources, abundant food, and den sites. They make dens in rock crevices, hollow trees or logs, burrows, caves, mines, old buildings, rain sewers, or other cavities for winter shelter and birth.

As opportunistic omnivores, Raccoons will eat both plant material and animals. They feed on practically anything they can fit in their mouths. Interestingly, in areas where food is abundant individual raccoons have been known to develop specific food preferences. Raccoons in urban locations are often larger than those in unpopulated areas because they have adapted to live on human hand-outs, pet food, and trash. They also generally have the benefit of fewer predators.
The second part of the Raccoon’s Latin name, “lotor,” translates to “washer,” referring to a unique behavior they exhibit. They often pick up food items and rub them with their paws, sometimes removing unwanted parts. This gives the appearance that they’re washing their food.
Lastly, they have REALLY cute babies. 🙂

#13. River Otter
- Lontra canadensis

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults grow 3 to 4 feet in length, including their tails.
- Their thick, protective fur is dark brown on the body and lighter brown on the belly and face.
- They have short legs with webbed feet, a long narrow body, and a long, muscular tail.
North American River Otters are semi-aquatic mammals that have an extensive range. They’re found in lakes, rivers, marshes, and estuaries in cold and warm climates. River Otters create dens along the shore that have entrances underwater. They forage at night but can be seen at all times of the day.
River Otters are lively, playful animals and are sometimes even spotted sliding around in the mud or snow. These activities help them to form social bonds and practice hunting techniques.
They use their long whiskers to detect prey in dark water, often grabbing a meal before the victim knows what’s happening. River otters are excellent swimmers, divers, and quick runners. They can stay underwater for up to eight minutes and run 18 miles per hour.
During the 19th and 20th centuries, river otters were heavily trapped and hunted for their fur to near extinction. Conservation and reintroduction efforts are helping many populations to recover; however, some northern populations are still considered vulnerable or imperiled. River Otters continue to face threats from water pollution and habitat destruction.
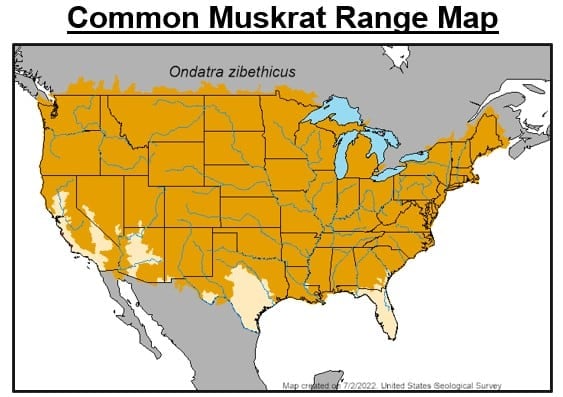
#14. Common Muskrat
- Ondatra zibethicus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 16 to 25 inches in total length and weigh 1.5 to 4 pounds.
- Their coloring is blackish-brown on the back, lighter brown with a reddish tinge on the sides, and pale on the underside.
- They have short front legs with small feet, strong hind legs with large, partially-webbed feet, and a vertically flattened, scaly tail.
Muskrats are one of just a few semi-aquatic mammals in Florida.
They occupy marshes, streams, ponds, rivers, and lakes with fresh and brackish water. This species lives in dens built into riverbanks or lodges they construct from sticks. Muskrats construct homes with underwater tunnels and dry, above-water chambers. Interestingly, they will sometimes move into occupied beaver lodges and cohabitate with them.
Being mostly omnivores, Muskrats typically feed on aquatic plants such as cattails, water lilies, and duckweeds. But when food is scarce, they sometimes eat other animals, including crayfish, snails, frogs, insects, and fish.
Muskrats are an important part of the ecosystem in the Florida panhandle, helping keep areas of marshes open and creating essential habitats for waterfowl. Unfortunately, this species was introduced to Europe as fur stock and has become invasive in many countries. They cause issues by burrowing into dikes and levees and causing flooding.
#15. Eastern Gray Squirrel
- Sciurus carolinensis

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are 16.6 – 21.6 inches (42 – 55 cm) long.
- Their coloring is gray-brown on the back and sides, with a white belly.
- This species has an extremely bushy tail, pointed ears, and a narrow face.
Many people battle with these small mammals in Florida at their bird feeders!
Eastern Gray Squirrels eat various foods, but naturally, their favorites are nuts, such as acorns, walnuts, and hazelnuts. As winter approaches, Eastern Gray Squirrels start hiding food in many locations, which provides them nutrition through the colder months. They hide more food than they will ever find, and some extra seeds will eventually grow into new trees. Who knew that squirrels could play such an important role in seed dispersal?
Eastern Gray Squirrel Range Map

Many people have thrown up their hands in defeat as they try to stop these acrobatic mammals from taking over the bird feeders in their backyard. Eastern Gray Squirrels LOVE birdseed and are relentless when they know an easy meal awaits inside a feeder. Their favorite foods include sunflower seeds, peanuts, and corn.
- RELATED: The 3 Types of Squirrels in Florida!
Some gray squirrels are black! Yes, I realize it’s strange that some Eastern Gray Squirrels have black fur, but it’s true! These black squirrels appear as a morph, and genetically speaking, it’s believed to result from a faulty pigment gene. No one is sure why the black morph evolved, but several theories have been offered. For example, some scientists think it may be a selective advantage for squirrels that inhabit the northern ranges to help them absorb heat.

- RELATED: Watch my LIVE animal cameras on Youtube! (You may see an Eastern Gray Squirrel right now in my backyard)
#16. Fox Squirrel
- Sciurus niger

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are 17.7 – 27.6 inches (45 – 70 cm) long.
- They have gray-brown fur on the back and orange bellies.
- This species has bushy tails, rounded ears, and large black eyes.
Fox Squirrels are the largest tree squirrel in Florida.
These small mammals can adapt to many different habitats in Florida. However, they are most often found in small patches of deciduous forests that include trees that produce their favorite foods, which are acorns, walnuts, pecans, and hickory nuts. To prepare for winter, they hide caches of these nuts all over the place to be eaten later when the weather turns cold.
In addition, Fox Squirrels thrive living around people. Consequently, they are commonly found in urban parks and neighborhoods.
Fox Squirrel Range Map

You will likely see Fox Squirrels foraging on the ground, as they spend much of their time there. But don’t let this fact fool you since they are still skilled climbers. In addition to scaling trees, they will easily climb a bird feeder pole to access birdseed. 🙂
#17. Brown Rat
- Rattus norvegicus

Look for Brown Rats anywhere people are living, particularly in urban environments. They’re best known for living in sewer tunnels and subway systems, scavenging food from the trash.
Believe it or not, this small mammal isn’t native to Florida. It’s thought to have originated in China and Mongolia.
Although many people find rats off-putting, others keep a sub-species of Brown Rats as pets. This subspecies, called the Fancy Rat, was bred specifically for the pet trade. Besides companion animals, rats can be trained for many jobs to assist humans, like detecting gunpowder for forensic teams and providing therapy support.
It’s a misconception that Brown Rats spread bubonic plague. In actuality, it’s more commonly spread through ground squirrels! Regardless, they can transmit infections of many kinds, as their blood can carry several diseases.
#18. Black Rat
- Rattus rattus

Interestingly, this small mammal is not native to Florida.
Instead, it’s thought that the Black Rat came from India and was transported to North America on cargo ships. It’s now so widespread that it’s no longer considered a foreign species.
It’s considered a pest in the agricultural market because it feeds on various crops. Like other rodents, Black Rats can carry pathogens in their bodies. While they may not appear sick, they can spread infections like toxoplasmosis, typhus, and bubonic plague.
In many areas where the Black Rat was once the dominant species, the Brown Rat has taken over. Black Rats are slightly smaller and reproduce less often, two of the reasons this species isn’t as widespread as Brown Rats.
#19. House Mouse
- Mus musculus

Few mammals in Florida thrive around people as well as the House Mouse!
House Mice have the characteristic large ears, thin tails, and tiny bodies of a typical “mouse.” They do incredibly well in highly populated areas, and there are now more semi-tame populations than wild.
House Mice are the most common species to find inside your home because they’re adaptable to human presence. They readily eat food scraps, build their nests in walls or dark attics and basements, and spend most of their time hidden from view. You’ve likely shared your home with a House Mouse at least once over the years. Although most people would prefer not to have them, they aren’t the worst roommates!
Like their eating habits, they are adaptable in their social behavior. House Mice with an excess of food, like those living in buildings, form a hierarchy with leaders and followers. However, in the wild, where food is less plentiful, females aggressively protect their territory from one another.
#20. 9-Banded Armadillo
- Dasypus novemcinctus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are about 2.5 feet long from nose to tail and weigh approximately 12 pounds.
- Their back, sides, head, tail, and outer legs are covered in bony, armor-like plates connected by flexible bands of skin.
- Tough skin and coarse hair cover the underside.
This species is one of the most unique-looking mammals in Florida!
A common misconception is that 9-Banded Armadillos roll up into a ball when threatened. One certain armadillo species can accomplish this feat. In reality, this species is much more likely to burrow for protection.
9-Banded Armadillos have an incredible system of reproduction. Every time this species gets pregnant, the zygote splits into four identical quadruplets! They’re the only animal that produces offspring this way, and scientists aren’t sure why it happens.
Unfortunately, because of their habit of digging into lawns, many people either harm or kill them. In addition, they’re also killed often by vehicles when crossing roads. So if you find a 9-Banded Armadillo, remember to observe it from a distance and appreciate what an amazing creature you’ve witnessed!
#21. American Beaver
- Castor canadensis

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are 29 to 35 inches long, with a tail length between 7.9 and 13.8 inches, and weigh between 24 and 71 pounds.
- They have a dark brown coat of waterproof fur, webbed feet, and a large, flat, black tail.
- Their large, continuously growing incisors (teeth) are orange due to thick layers of enamel.
The American Beaver is North America’s largest rodent!
These incredible mammals are known as ecosystem engineers, meaning they’re one of just a few species that actively work to alter their habitat. They do so by building dams with trees, branches, and mud. Beavers use the dams for shelter, food storage areas, and dens for raising young.
Ponds created by beaver dams serve as important habitats for many types of wildlife. They also help reduce erosion and slow water movement, promoting moisture in drought-prone areas. Especially in northern climates, the water in the pond needs to be deep enough that it doesn’t freeze solid, allowing the beavers to swim under the ice all winter.
Beavers are excellent swimmers and can stay submerged for up to 15 minutes. They spend as much time as possible in the water, where they are less vulnerable to predators. This species uses its large tail to slap the water to signal danger to other beavers, as well as fat storage.
#22. Virginia Opossum
- Didelphis virginiana

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults measure 13 to 37 inches in length.
- Their fur is whitish underneath and dull grayish-brown on top though it varies throughout their range.
- They have white faces, long, hairless tails, and feet with opposable thumbs.
The Virginia Opossum is the only marsupial mammal in Florida!
They occupy various habitats but generally prefer forests and thickets near a source of water. This species adapts well to human presence, so you’re likely to find them in rural, suburban, and urban environments, including your yard.
Although many people consider the Virginia Opossum a pest, they provide an important service to humans! Insects, including ticks, are a staple food for opossums. They’re incredibly good at grooming and eat 95% of ticks that try to feed on them, up to 5,000 ticks in a single season. So, the next time you’re worried that an opossum is roaming your yard, remember they reduce your chances of tickborne illness.
This species is known to play dead or “play possum,” a unique tactic they’ve become known for. They go into a catatonic state, drool, and exude a noxious substance from their anal glands, feigning death.
As marsupials, Opossums give birth to relatively undeveloped young, which they carry in a pouch on their belly until they’re more developed. The young opossums are only about the size of a kidney bean, but they crawl into the pouch without assistance. Even though litters can be made up of 25 babies, only a small percentage survive.
#23. American Mink
- Neogale vison

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults measure between 12 and 18 inches long, have 6 to 10-inch tails, and weigh between 1 to 3 pounds.
- They have a long sleek body, short stubby legs, long neck, small ears and eyes, slightly webbed feet, and a long thick tail.
- Their fur is brown to black, soft, thick, and covered with oily guard hairs that make it waterproof.
The small mammals can be found in Florida in forested areas near large water sources. Their dens are located on river banks, under logs and tree stumps, or at the base of trees. Their dens are always close to water.
Minks are voracious predators and feed on surprisingly large prey. Believe it or not, they can eat fish up to 12 inches long and kill coastal birds like seagulls and cormorants by drowning them. Their slightly webbed feet and streamlined bodies are powerful in the water, and they can swim for up to three hours without stopping! While they’re rarely far from water, they hunt on land and can climb trees.
Despite this species being regularly hunted for its fur, its population is stable. However, scientists have expressed concern about the effect of escaped domesticated Minks on wild populations. Released Minks can cause territorial issues with wild populations and may introduce weaker genetics by breeding with wild individuals.

Check out the video of a mink above!
#24. Big Brown Bat
- Eptesicus fuscus

Identifying Characteristics:
- Larger-sized bat with around a 12-inch wingspan.
- Brown fur with black ears, wings, and feet. Wings are hairless.
These flying mammals are widespread in Florida.
If you know where to look, you’ll find Big Brown Bats inside caves, tunnels, or other human structures.
Big Brown Bat Range Map

This nocturnal bat primarily eats insects, especially ones that fly at night. However, their preference is to eat beetles. The Cucumber Beetle is their favorite, which benefits farmers because these insects are terrible pests for agriculture. Many farmers in Florida even use bat boxes to attract Big Brown Bats to their property!
Though rabies is common in all bats, research has shown the disease is rarer in this species. The reason for this fact is that many Big Brown Bats have immunity to rabies. Interestingly, researchers discovered that these rabies antibodies get passed down from generation to generation!

If you want even more information about mammals, or need help with additional identification, check out this field guide!

Which types of mammals have YOU seen in Florida?
Let us know in the comments!